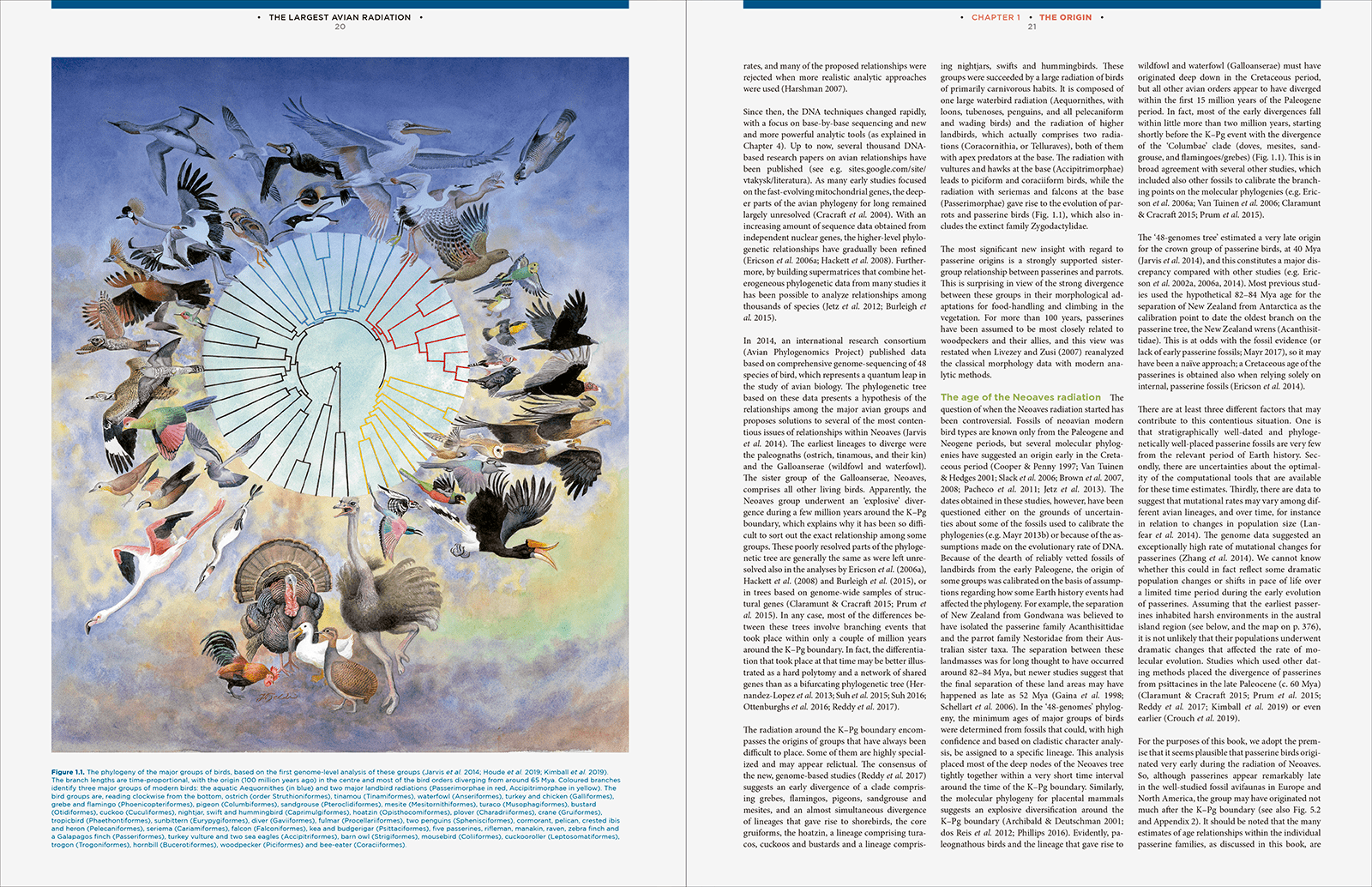
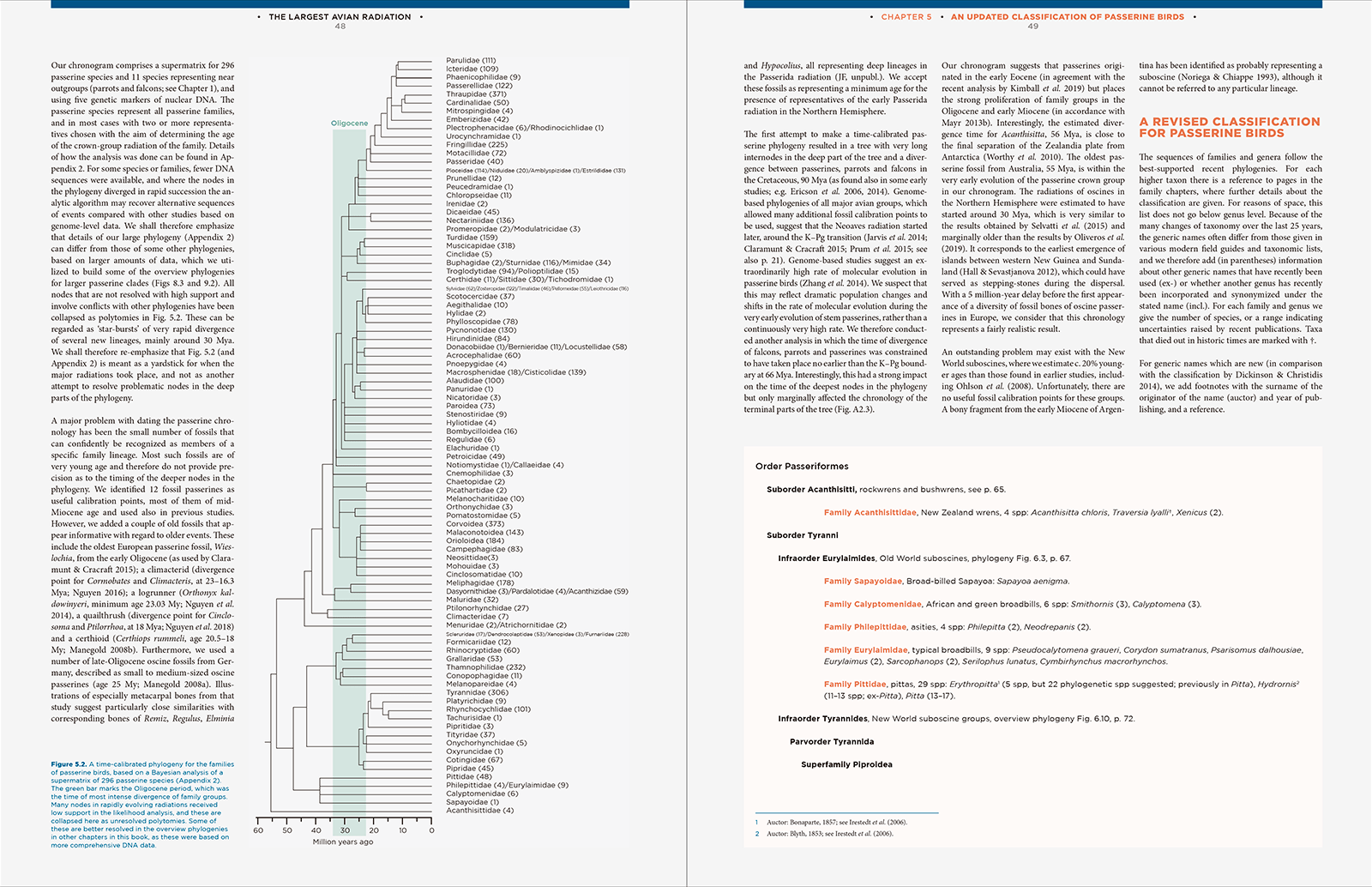
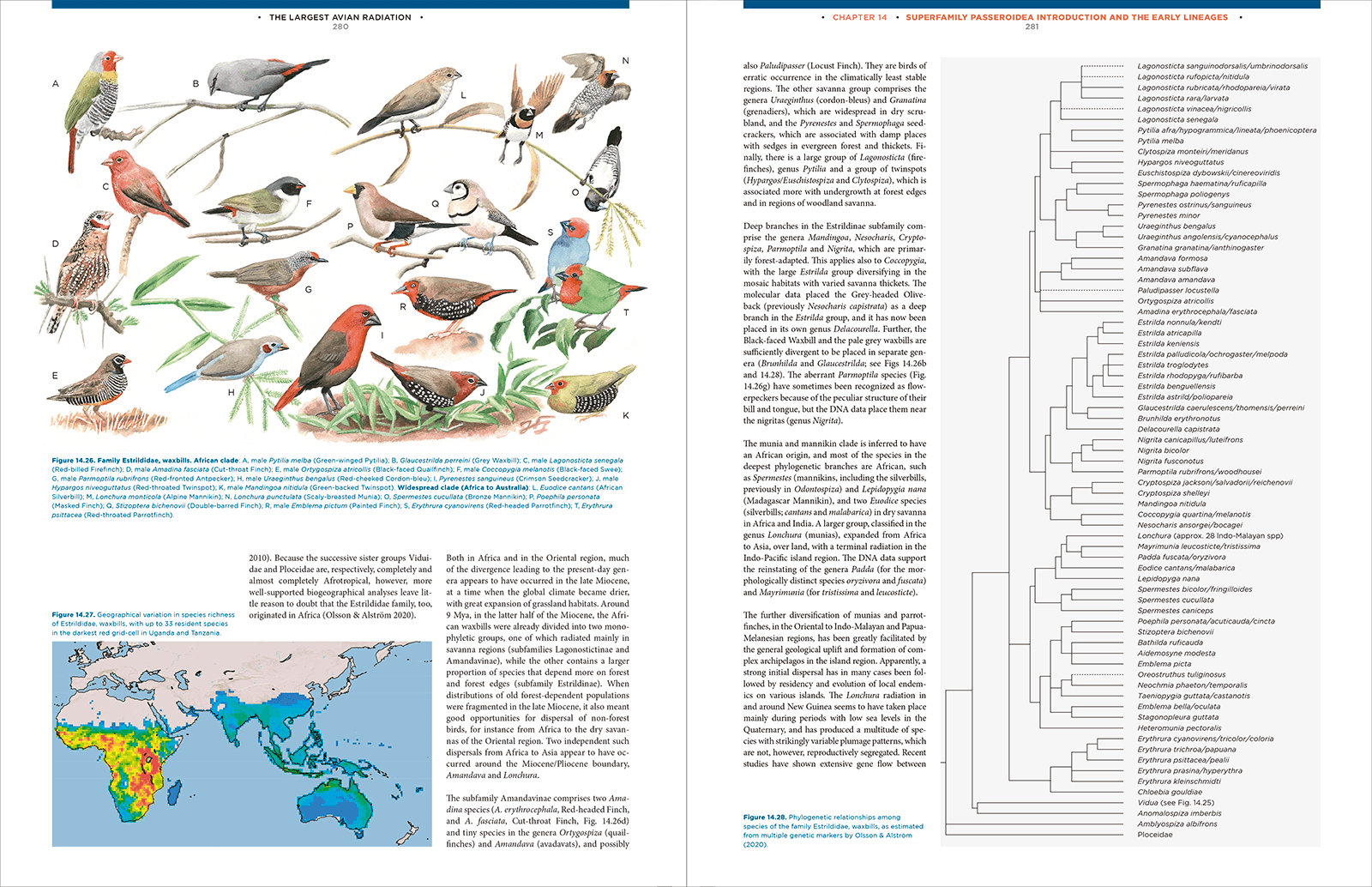
The Largest Avian RadiationThe Evolution of Perching Birds, or the Order Passeriformes
El preu original era: $108.80.$97.92El preu actual és: $97.92.
En estoc
El preu original era: $108.80.$97.92El preu actual és: $97.92.
Pes
2.6 kg
Dimensions
24 × 31 cm
Idioma
Anglès
Format
Tapa dura
Pàgines
445
Data de publicació
November 2020
Publicat per
Lynx Edicions
Descripció
Amb més de 6.200 espècies, els ocells posats (o passeriformes) representen una de les proliferacions d’espècies més notablement ràpides. La classificació tradicional dels ocells, que es basava principalment en estudis anatòmics comparatius realitzats fa més de 100 anys, no podia fer gaire per resoldre les relacions entre els passerells perquè generalment eren massa uniformes anatòmicament. Per tant, la classificació que es va utilitzar durant la major part del segle XX va ser una disposició pràctica, on els milers d’espècies es van acomodar en uns quants grups amplis basats principalment en adaptacions ecològiques.
Estudis recents d’ADN han canviat dràsticament la comprensió de les relacions evolutives dels passerells. Pel que sembla, els passeriformes es van originar durant les primeres radiacions dels ocells moderns, als continents australs (Amèrica del Sud, Antàrtida i Austràlia), després que una catàstrofe global hagués acabat amb la major part de la vida terrestre antiga, inclosos els grans dinosaures i els primers ocells.
Aquest llibre revela la nova història notable de com els passerells es van diversificar i es van dispersar per tot el món. També presenta i explica la nova classificació, que reflecteix la història filogenètica. Els nous coneixements revelen que molts dels antics llinatges evolutius comprenen només unes poques espècies que van romandre a la seva àrea d’origen o van patir una dispersió limitada. Només un nombre reduït de grups van experimentar una proliferació significativa de noves espècies i només cinc (de 145) famílies de passeriformes estan representades a tots els continents excepte a l’Antàrtida. Tot i així, la variació global de la riquesa d’espècies generalment es correlaciona bé amb la variació de la productivitat entre diferents entorns. Veiem com és possible una taxa global d’evolució aparentment constant de noves espècies a causa de la ràpida proliferació en nous nínxols ecològics, inclosos els arxipèlags, i una extraordinària acumulació d’espècies endèmiques en determinades serralades tropicals.
A més de descriure la història evolutiva revisada dels ocells paseriformes, els autors intenten identificar els canvis adaptatius, inclosos els canvis en les estratègies de la història de la vida, que són la base de les grans expansions evolutives. El seu objectiu és fomentar el desenvolupament d’una teoria unificada per explicar com es genera la variació prodigiosa de la biodiversitat de la Terra.














 Copyright 2026 © Lynx Nature Books
Copyright 2026 © Lynx Nature Books
Gehan de Silva Wijeyeratne –
This book is an excellent example of how to make deep science less intimidating. I had wondered how Lynx Edicions that had carved a niche for being at the interface between hard science and popular natural history would tackle a subject that would appear to most people to be dense and impenetrable. Superb design and excellent writing and editing have resulted in a book which not only keen birders but others interested in topics such as speciation and biogeography would find interesting.
The first thing that strikes you about the book is the design. Chapters and section headings are announced in capital letters in bright colours. There is generous use of delightful bird illustrations (by the multi-talented Jon Fjeldså, the lead editor) which although accurate have a lightness that leans towards arty than illustrative. All of this creates the right ‘mood music’ for anyone who may have been otherwise intimidated by the prospect of delving into the details of molecular phylogenetics.
Over the years, many books, in particular those in the excellent Helm Family Monograph series have included introductory sections or chapters explaining molecular phylogenetics. Many books on birders’ bookshelves also contain the branching diagrams or phylogenetic trees arising from genetic studies. Furthermore, attendees of popular talks at the more serious end of ornithology are also used to discussions on molecular phylogenetics. Technical knowledge in the world of birding has come a long way in the last few decades and I suspect most birders will be comfortable with the vast majority of the text in this book. However, I would caution this is not a book for everyone with an interest in birds. You need to be someone who is already following with interest, the science behind splits and lumps at species level to follow the discussions in this book although the book is focussed at the higher taxonomic levels of families.
The book is in three sections. Most people may find that this book can be approached by reading ‘Section 1 Background’ followed by ‘Section 3. Thematic chapters’. At the core of the book is ‘Section 2. Classification and families of passerine birds’ (pages 45- 318). Section 2 begins with an ‘An Updated Classification of Passerine Birds’ which discusses past attempts to classify the passerines and concludes with a new family tree that shows various higher taxonomic levels including suborders, infraorders, parvorders, superfamilies, subfamilies and families. The design is excellent and uses indentation, boldfacing and colours to help with easy and comfortable visual navigation. Chapters 6 to 14 discuss each family of passerines. The families are grouped in the chapters under higher taxonomic groupings. For example, chapter 8 is titled the ‘Cohort Corvoides: the crow like passerines’. Whether you have a special interest in a family, or doing some background reading in anticipation of seeing new families on a forthcoming birding trip or one of the growing band of birders who are trying to see every bird family, these chapters will be of absorbing interest, provided you are not fazed by a sciencey text. If the presence of bracketed citations and the phylogenetic diagrams are ignored, almost all of the text is readable to a keen birder of the sort who would be subscribing to a journal like ‘British Birds’. Occasionally a family account may have extensive discussion on revisions based on molecular phylogenetics; examples include the sunbirds and tanagers. Admittedly, these can be heavy reading.
Although this is a book on passerine birds, the first four chapters will be useful reading to anyone with an interest in any animal groups, especially vertebrates. There is useful background information here on systematics and taxonomy and forces behind evolutionary change. We also learn of the important role of New Guinea as a staging post for the passerines to spread across the world from an origin in the Southern Hemisphere. ‘Section 3. Thematic chapters’ (pages 319 to 369) and the first of two appendices (on a short earth history) also have useful background information. Chapter 15 on ‘The worldwide variation in biodiversity: some central questions and concepts’ and chapter 16 on ‘How new species evolve’ with their chapter headings, give a clear sign on the many interesting topics that are covered in these chapters. Having lived on islands, discussions on speciation models are of particular interest to me. But even a large continent like Africa has over geological time functioned as a patchwork of ecologically isolated areas or islands which has given rise to a number of endemic animals which are confined to limited areas. Island geography or more generally geographical isolation is not the only factor in speciation and chapter 16 also discusses factors such as song in the speciation process. One thing I would have liked to have seen included is a Geological Time Scale. I printed one off the internet to make it easier for me to follow some of the time scales discussed in various chapters.
The references in the end sections are extensive (pages 397 to 432) and reinforce the point that this book is a synthesis of the work of over a thousand papers published on passerine molecular phylogenetics. But as the editors note, this is only a stock take of work done so far and further advances will arise from whole genome sequencing. The lack of a good fossil record and other issues in constructing a molecular phylogeny means that the exact placement of some avian families is still uncertain. An example being the Kinglets or Crests (family Regulidae). This is a family I am familiar with as its members include the Goldcrest, a bird I encounter in parks with conifers in London. As with many family accounts, there is an evocative introduction to the family followed by the nitty gritty of molecular phylogenetics. In this case the surprising conclusion is that the placement of the family is still unresolved. All birders have their favourite bird families and will find it easy to be absorbed by the family accounts of their favourite families.
On the whole it is a remarkable book for its contribution of deep science and insights made accessible to serious birders through good writing and design. I suspect no other group of biological organisms has a cutting edge science book of this genre devoted to it that is aimed at a popular market. The book also casts a light on birders as being a sociological phenomenon. Birders are an economically very valuable group of hobbyists who number in the several hundred thousand and are a subset of a few million birdwatchers world-wide. They generate millions of dollars in revenue for industry sectors from tourism to publishing. But interestingly, probably no other special interest group of this number of adherents follows the outcomes of cutting edge science with such keen interest.